Analisi completa dei vantaggi e delle sfide delle microreti
Data di rilascio: 24-11-2025
Con l'accelerazione della transizione energetica globale, le microreti, in quanto soluzione emergente per i sistemi energetici, stanno guadagnando sempre più attenzione. Microreti Sono considerate un modo efficace per migliorare l'efficienza elettrica e ridurre la dipendenza dalle reti tradizionali. Consentono la generazione e la distribuzione localizzata di elettricità, migliorando la flessibilità e l'efficienza nella gestione energetica. Nonostante i numerosi vantaggi delle microreti, l'implementazione di questa tecnologia emergente deve ancora affrontare una serie di sfide.
In questo articolo verranno esaminati in modo approfondito i vantaggi delle microreti, i loro principi operativi e le sfide che si possono incontrare durante la loro implementazione.
Sommario
Cos'è una microrete?
Una microrete è una piccola rete elettrica indipendente in grado di generare, utilizzare e gestire l'elettricità a livello locale. A differenza delle tradizionali reti su larga scala, le microreti possono funzionare sia connesse alla rete pubblica che in modalità isola quando sono disconnesse dalla rete. Questa flessibilità di alimentazione rende le microreti uno strumento importante per contrastare i guasti della rete, i picchi di domanda e le sfide ambientali.
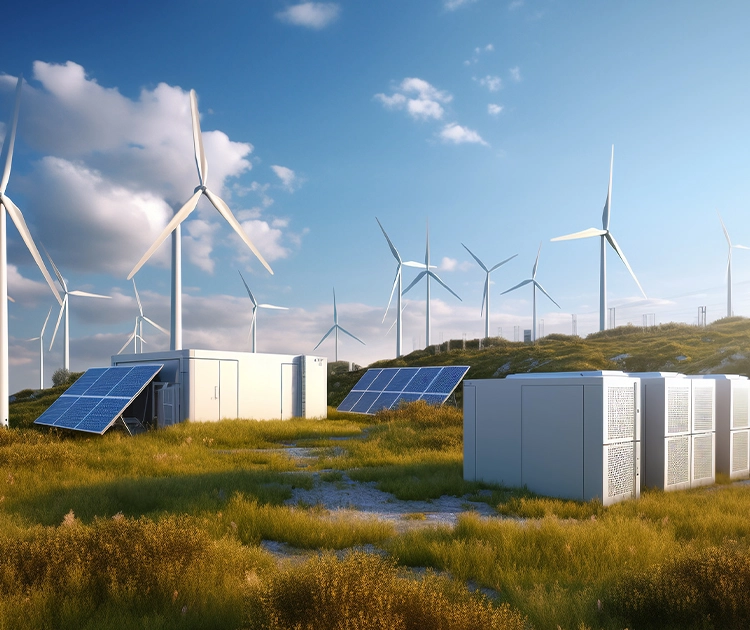

Come funzionano le microreti?
Il fulcro di una microrete risiede nella concentrazione della produzione e del consumo di energia nello stesso luogo, riducendo le perdite di trasmissione associate alla trasmissione di energia a lunga distanza nei sistemi tradizionali. Le microreti possono generare elettricità attraverso diverse combinazioni di energia, tra cui solare, eolico e generatori diesel di riserva. Inoltre, le microreti sono in genere dotate di sistemi di accumulo di energia (come le batterie) che immagazzinano l'energia in eccesso e la rilasciano durante i picchi di domanda o le interruzioni della rete.
I sistemi di controllo intelligenti consentono alle microreti di regolare l'alimentazione elettrica in modo flessibile in base ai dati in tempo reale. Ad esempio, possono passare automaticamente alla rete pubblica durante i periodi di picco o passare alla modalità isola in caso di guasto, garantendo un'alimentazione elettrica continua e affidabile.
Vantaggi delle microreti
1. Benefici ambientali
Uno dei maggiori vantaggi delle microreti è la promozione delle applicazioni di energia rinnovabile. Integrando fonti di energia pulita come l'energia solare ed eolica, le microreti riducono significativamente la dipendenza dai combustibili fossili, riducendo così le emissioni di gas serra e contribuendo alla mitigazione dei cambiamenti climatici. Inoltre, poiché la produzione e il consumo di energia sono più localizzati, aumenta l'efficienza energetica e si accresce la consapevolezza ambientale degli utenti.
2. Costi energetici ridotti
Grazie alla generazione localizzata, all'accumulo di energia e alla programmazione intelligente, le microreti possono ridurre efficacemente i costi dell'elettricità. Rispetto alle reti tradizionali, le microreti riducono al minimo le perdite di trasmissione e distribuzione, ottimizzando l'uso dell'elettricità. Inoltre, durante i periodi di picco dei prezzi dell'elettricità, le microreti possono regolare il consumo energetico attraverso meccanismi di risposta alla domanda, riducendo ulteriormente la spesa elettrica.
3. Affidabilità dell'alimentazione migliorata
Nelle reti centralizzate tradizionali, sovraccarichi o guasti alle apparecchiature causano spesso interruzioni di corrente diffuse. Tuttavia, quando una microrete subisce un guasto, può passare automaticamente alla modalità isola, continuando a fornire energia agli utenti. Questo è particolarmente importante per l'alimentazione di ospedali, data center e altre infrastrutture vitali, garantendo una fornitura elettrica stabile durante le emergenze.
4. Maggiore resilienza del sistema
I sistemi di microreti hanno una forte resilienza alle emergenze. Che si tratti di rispondere a disastri naturali, attacchi informatici o altri eventi imprevisti, le microreti possono continuare a funzionare stabilmente anche in caso di guasti locali. La capacità di operare in modo indipendente garantisce che, anche in caso di guasto di una parte della rete, altre sezioni possano continuare a funzionare normalmente.
5. Efficienza energetica migliorata
Le microreti contribuiscono a ottimizzare l'uso dell'energia. Localizzando la generazione e utilizzando sistemi di controllo intelligenti, le microreti possono utilizzare l'energia in modo più efficiente. Ad esempio, integrando la tecnologia di cogenerazione (CHP), le microreti possono non solo fornire elettricità, ma anche recuperare e utilizzare il calore prodotto durante la generazione, migliorando l'efficienza energetica complessiva.
Le sfide che devono affrontare le microreti
1. Elevati costi di investimento iniziale
La costruzione di una microrete richiede un elevato investimento iniziale, che include l'acquisto di apparecchiature di generazione, sistemi di accumulo e sistemi di controllo intelligenti. Questo può rappresentare un onere finanziario significativo per alcune comunità o aziende. Sebbene l'esercizio a lungo termine possa generare benefici economici, l'elevato costo iniziale può scoraggiare i potenziali utenti. Le politiche di sostegno finanziario e di sussidi governativi, in particolare quelle che promuovono gli investimenti in energia verde, possono contribuire a ridurre l'onere finanziario iniziale.
2. Problemi di integrazione e standardizzazione della tecnologia
Le microreti utilizzano diverse tecnologie, come l'energia solare, l'energia eolica, l'accumulo di energia tramite batterie e sistemi di programmazione intelligenti. Garantire l'efficace integrazione e compatibilità di queste diverse tecnologie rappresenta una sfida tecnica. Attualmente, la mancanza di standard e protocolli unificati può compromettere l'interoperabilità dei sistemi di microreti. Pertanto, promuovere la standardizzazione tecnologica, unificare i protocolli di comunicazione e le interfacce dei dispositivi è fondamentale per promuovere e diffondere le microreti.
Mancanza di conoscenze tecniche ed esperienza
Essendo una tecnologia emergente, le microreti richiedono elevati requisiti tecnici per il funzionamento e la gestione. La mancanza di personale qualificato ed esperto, soprattutto nelle aree remote, può aumentare la difficoltà di gestione e manutenzione del sistema. Per garantire un funzionamento stabile delle microreti, sono necessarie una ricerca tecnica approfondita e l'accumulo di esperienza, oltre allo sviluppo di strumenti di monitoraggio e gestione adeguati.
Sfide normative e politiche
L'attuale quadro normativo in materia di energia si basa principalmente sulle reti elettriche tradizionali e non tiene pienamente conto dell'unicità delle microreti come nuovo sistema elettrico. Di conseguenza, mancano chiare linee guida normative per l'implementazione delle microreti. Per promuovere l'applicazione diffusa delle microreti, i governi devono elaborare nuove politiche e normative che ne supportino il funzionamento e lo sviluppo, nonché risolvere i problemi di coordinamento con i sistemi elettrici esistenti.
Sfide nell'espansione
Le microreti sono in genere progettate per aree di piccole dimensioni o gruppi di utenti specifici, come un campus, un edificio o un parco industriale. Questo modello di alimentazione elettrica su piccola scala potrebbe non soddisfare le esigenze di regioni o comunità più grandi. Pertanto, la scalabilità e la sostenibilità delle microreti rimangono questioni che necessitano di ulteriori approfondimenti.
Conclusione
Le microreti stanno trasformando il panorama dell'approvvigionamento energetico. Non solo migliorano l'efficienza energetica e riducono i costi, ma aumentano anche significativamente l'affidabilità e la resilienza dei sistemi di alimentazione. Sebbene le microreti affrontino sfide in termini di tecnologia, politiche e finanziamenti, con i progressi tecnologici e il crescente sostegno politico, le microreti svolgeranno senza dubbio un ruolo importante nel futuro sistema energetico.
Tecnologia JN si impegna a fornire servizi leader soluzioni tecnologiche per microreti Per aiutare i clienti a raggiungere una gestione energetica più efficiente e sostenibile. Continueremo a promuovere l'innovazione e lo sviluppo nella tecnologia delle microreti, offrendo soluzioni di alimentazione sostenibili ed efficienti agli utenti di tutto il mondo.